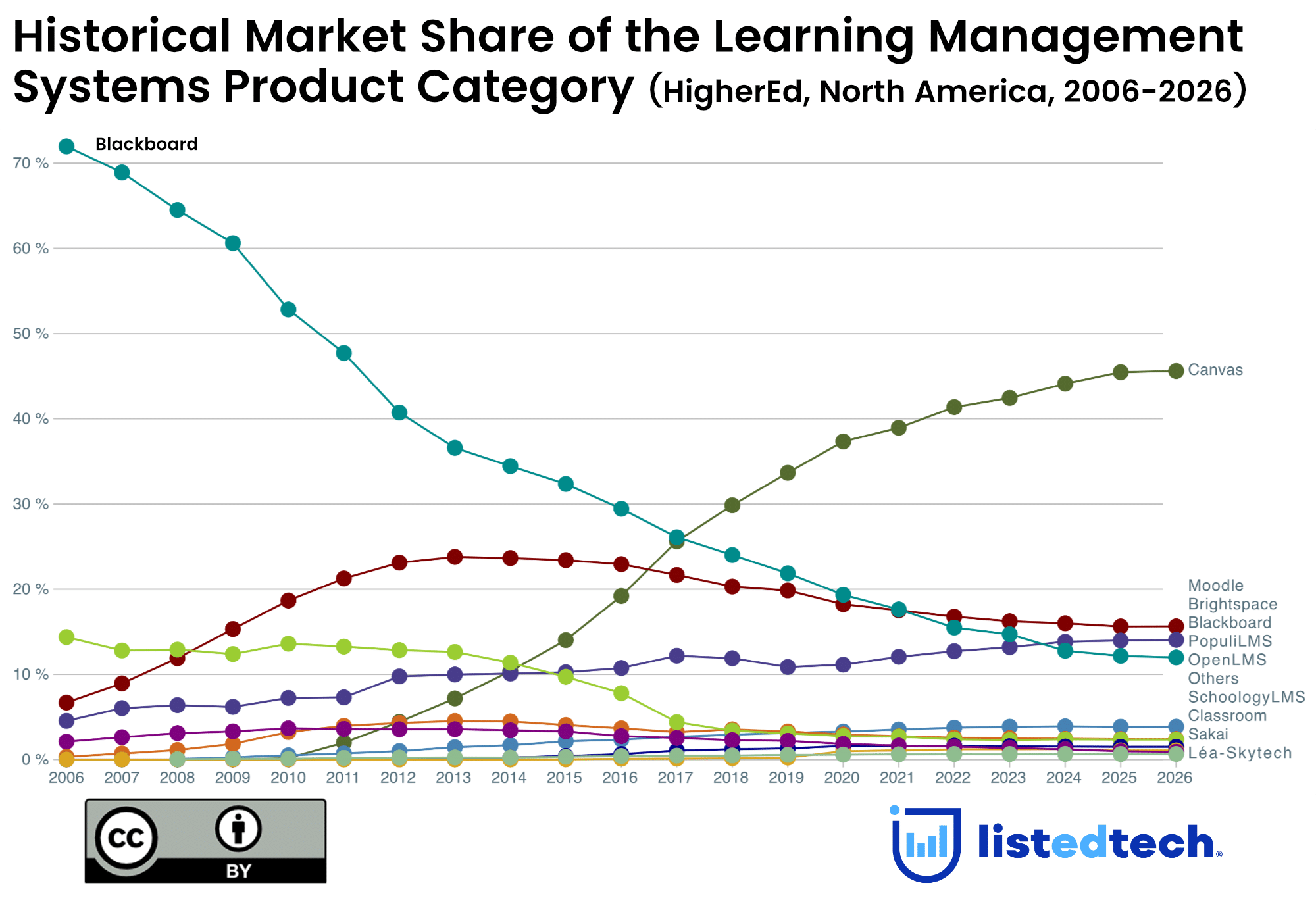
Regarding payment solutions, universities, colleges and school districts are no different from your local coffee shops, department stores or movie theatres: they need an easy way to exchange money to pay for goods and services. A few years ago, cash was the only way to pay tuition fees. These times are long gone, especially since the Covid-19 pandemic. This text presents the payment solutions category.
Definition
Payment solutions refer to the various methods and technologies individuals and businesses use to make and receive payments for goods and services. These solutions may include traditional methods, but educational institutions use newer digital payment methods like credit and debit cards and online payment platforms.
Banks, financial institutions, and payment processing companies provide payment solutions to their clients. Convenience, speed, and security are key priorities when designing payment solutions. We can see the payment solutions structure as a triad: the good or service, the financial institution and the business (in our context, the university, college or school district).
History of Payment Solutions
Before we swiped/inserted debit and credit cards daily, people used coins and notes long before financial institutions introduced cheques around the 1850s. However, we had to wait more than 100 years to see another revolution in this economic sector.
The first US company to introduce a credit card was Diners Club in 1950, followed by American Express (1958), Visa (1959) and MasterCard (1966). At the time, cashiers needed to phone the credit card company to ensure the card limit was not reached. Fortunately, at the end of the 1980s/early 1990s, major credit card companies implemented online authorization systems to ease cashiers’ work and, most notably, speed up the administrative process of issuing credit card bills each month.
Banks presented the payment card (debit card) to the public in 1966. At the time, Americans and Canadians used it to withdraw money at ATMs. The United States was an early adopter of the technology, with STAR, the first debit card network, in 1984. In Canada, as of 1994, paying in many stores, gas stations, and restaurants is possible using your bank card via the Interac network.
When telecommunication companies started to install an Internet connection in households around 1995, banks and credit card companies deployed online banking solutions to their clients. By the end of the century, Paypal offered secured online transaction payments to millions of Americans, Canadians and Europeans.
In the past decade, the evolution of payment technology didn’t stop. From the magnetic stripe to the chip to the contactless payment (NFC), paying for your pizza slice is easier than ever. This momentum didn’t only hit North America and Europe. African countries have also developed payment and electronic money transfers via SMS since the Internet, but personal computers are still challenging in some parts of the continent.
Educational institutions have also joined in. In 2000, students could only pay their tuition fees by cheques or in person. Today, some institutions receive payments via bank transfers, accept electronic transfers by email or SMS and do business with money transfer companies. Times have changed, and this is an excellent sign for both the students and the institutions.
Advantages of Using Payment Solutions in Education
Universities, colleges and school districts employ payment solutions to make financial transactions more convenient and secure. Some examples include:
- Tuition payments: universities and colleges offer online portals where students can pay using a credit or debit card or electronic funds transfer.
- Course fees and materials: on-campus libraries often propose e-commerce platforms to purchase course fees, textbooks, and other materials required for classes.
- Donations and fundraising: collect donations and funds for school-related events, projects, and initiatives are usually managed by payment solutions.
- Meal plans and campus services: many payment solutions include using NFC technology to add money to student cards. This includes meal plans, campus transportation services, and other services that require payment.
- Continuing education: online payment platforms can manage the payment for courses, seminars, and other professional development opportunities.
By using payment solutions in education settings, schools and universities can streamline financial transactions and reduce the burden on administrative staff. This saves time and money for both the institution and the students, as well as the families they serve.
Downsides of Payments Solutions
While payment solutions can provide benefits in an educational setting, some potential inconveniences are associated with using these services.
- Fees: like regular transactions in stores and restaurants, institutions must pay fees to accept transfers using payment solutions. When comparing traditional methods (cheques, in-person payments) with newer technologies, these fees can be bothersome for institutions. Smaller institutions are more at risk of suffering from this inconvenience.
- Technical issues: since they rely on technology, payment solutions can experience glitches and downtime. This situation can add to the stress of students and staff when approaching a payment deadline.
- Security concerns: payment solutions require students’ input of sensitive financial information. This information can be vulnerable to security breaches, leading to fraud or identity theft.
- Accessibility: international and remote students may have difficulty accessing the technology to use payment solutions, mainly if they come from disadvantaged backgrounds. This can create disparities in access and challenge these students to complete their payments.
Educational institutions need to consider these potential inconveniences and work to minimize their impact, particularly for students and families who may be most affected. For instance, if the payment solution used in an institution adds administrative fees on the student’s end, the institution should clearly state them on the appropriate webpage and the student’s tuition bill.
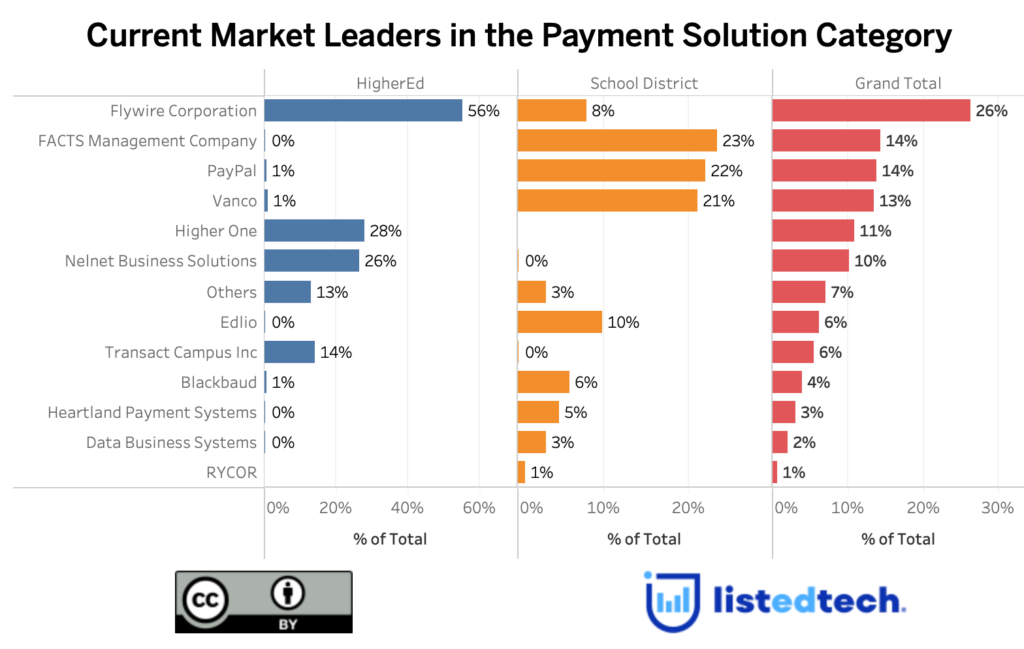
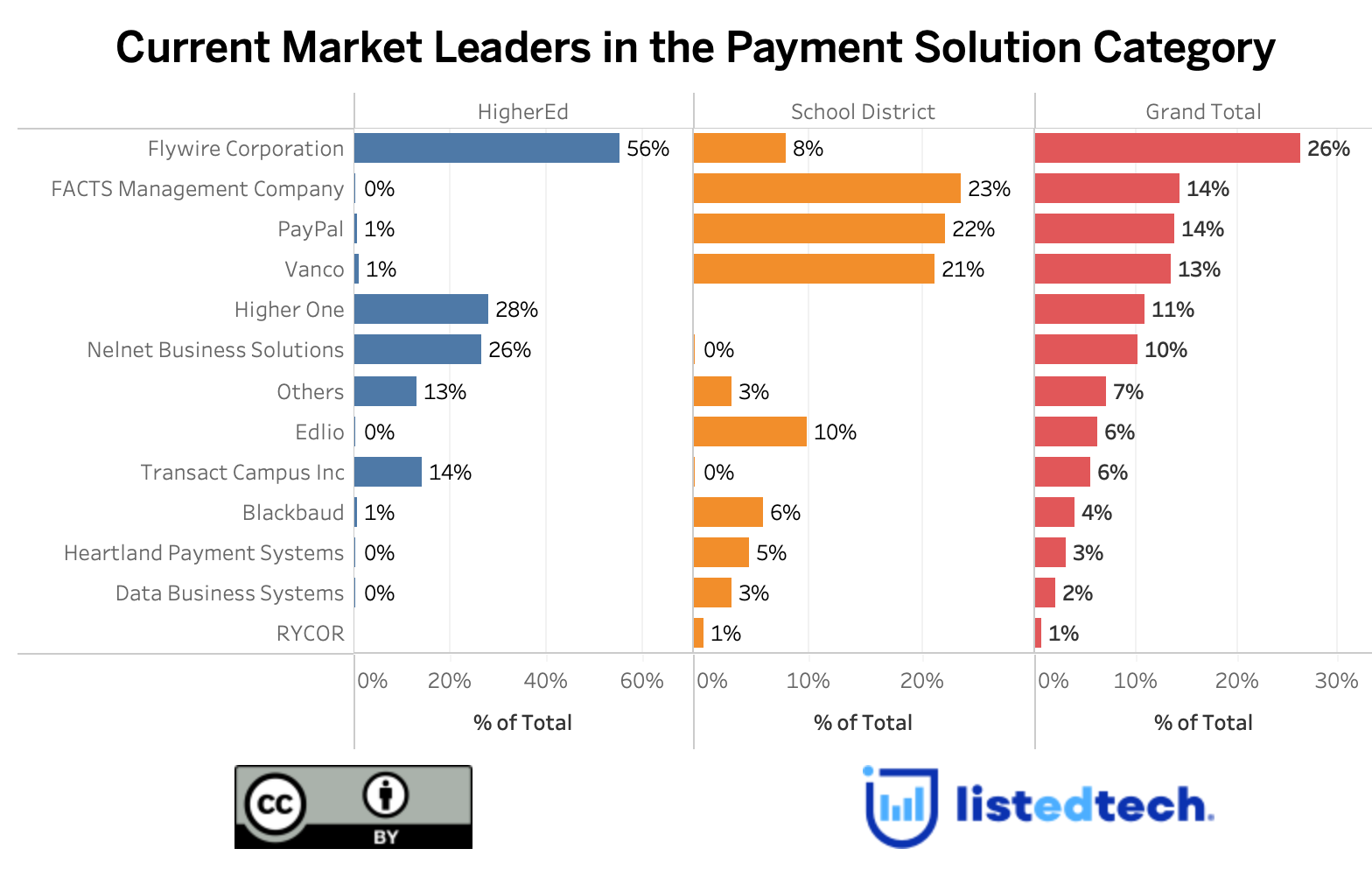
As demonstrated in the graph above, the payment solution category does not have a lot of systems used in both HigherEd and K-12 submarkets. A few examples: FlyWire markets itself as a “higher education payment solution,” FACTS has a K-12 Solution menu item and no HigherEd, and Transact identifies university clients and college case studies on its website.
Regarding the HigherEd submarket, Flywire Corporation leads the board with 56%, followed by Higher One (28%) and Nelnet Business Solutions (26%). On the K-12 side, FACTS Management is on the top of the podium (24%), followed by Paypal (22%) and Vanco (21%). The K-12 submarket seems tighter for the top-3 options, and we could see the leader changing in the near future.
The Future of Payment Solutions
The payment solution category will continue to grow and propose new solutions and technology features soon. Mobile payments will undoubtedly become a stake when suggesting new development avenues. We must mention the integration with learning management systems, especially for continuing education platforms and better integration of course material payment and delivery. Thanks to cryptocurrency, the rapid growth of blockchain in payment methods could mean a more extensive set of options for institutions when it comes to a more secure and transparent way to process payments (as well as store academic credentials and certifications). Finally, thanks to the technology provided by payment solutions, institutions could implement personalized payment plans for students in precarious financial situations and those receiving scholarships or bursaries.
Overall, the future of payment solutions in education is likely to be shaped by ongoing technological innovations and the need to provide students with more convenient, accessible, and affordable ways to pay for their education.